Evidence suggests periodontal disease may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and be a risk factor for 21 other diseases. Many people can go years without showing any symptoms at all, and others may not realize that they are in the early stages of gingivitis due to other dental problems. Untreated periodontal disease can become severe and lead to tooth loss.
What is gum disease?
Gum disease is an infection of the soft tissues surrounding the teeth. There are two stages of gum disease. The first is called gingivitis, and the second is periodontitis.
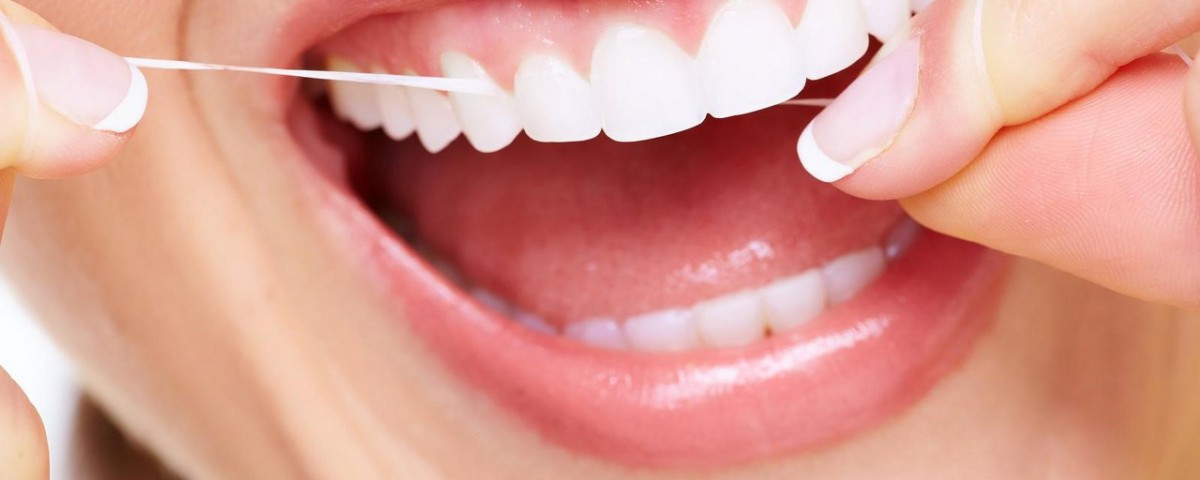
Gingivitis is the initial stage of periodontal disease is reversible with treatment. Affected gum areas become increasingly red due to the influx of blood to the area to try and fight the infection. They may appear swollen and may bleed easily, especially while brushing or flossing. The condition is reversible at this stage with regular brushing, flossing and visits to the dentist. If it is not treated however, gingivitis may lead to a more serious condition called periodontitis.
Periodontitis causes irreversible damage to the gums, bones and other structures that support the teeth and it can lead to tooth loss. The inflammatory process attracts immune cells and molecules to the site and, in later stages promotes the healing of infected tissues. However, treatment can help by stopping the advancement of the disease. At more advanced stages, the disease may require more complex treatment to prevent tooth loss. In the worst case, teeth can become loose and need to be removed by the dentist or worse yet, fall out on their own.